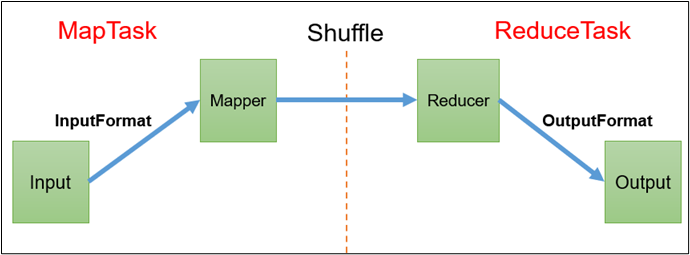
MapReduce概述
定义
MapReduce是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架
优缺点
优点:
- 易于编程
- 良好的拓展性
- 高容错性
- 适合PB级以上海量数据的离线处理
缺点:
- 不擅长实时计算
- 不擅长流式计算
- 不擅长DAG(有向无环图)计算
MapReduce进程
一个完整的MapReduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
MrAppMaster:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调。
MapTask:负责Map阶段的整个数据处理流程。
ReduceTask:负责Reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程。
常用数据序列化类型
| Java类型 | Hadoop Writable类型 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | BooleanWritable |
| Byte | ByteWritable |
| Int | IntWritable |
| Float | FloatWritable |
| Long | LongWritable |
| Double | DoubleWritable |
| String | Text |
| Map | MapWritable |
| Array | ArrayWritable |
| Null | NullWritable |
MapReduce编程规范
用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper、Reducer和Driver。
Mapper
- 用户自定义的Mapper要继承父类Mapper(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper)
- Mapper的输入数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
- Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中
- Mapper的输出数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
- map()方法(MapTask进程)对每一个<K,V>调用一次
Reducer
-
用户自定义的Reducer要继承父类(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer)
-
Reducer的输入数据类型对应Mapper的输出数据类型,也是KV
-
Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中
-
ReduceTask进程对每一组相同k的<k,v>组调用一次reduce()方法
Driver
相当于YARN集群的客户端,用于提交我们整个程序到YARN集群,提交的是封装了MapReduce程序相关运行参数的job对象
示例程序WordCount
Mapper
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
Text k = new Text();
IntWritable v = new IntWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 获取一行
String line = value.toString();
// 分割字符串
String[] split = line.split(" ");
// 输出
for (String s : split) {
k.set(s);
context.write(k, v);
}
}
}
Reducer
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
int sum;
IntWritable v = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 累加求和
sum = 0;
values.forEach(item -> {
sum += item.get();
});
// 输出
v.set(sum);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
Driver
public class WordCountDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1 获取配置信息以及获取job对象
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// 2 关联本Driver程序的jar
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
// 3 关联Mapper和Reducer的jar
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 4 设置Mapper输出的kv类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 5 设置最终输出kv类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 6 设置输入和输出路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:\\Documents\\test\\combine_input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\Documents\\test\\combine_output"));
// 7 提交job
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
集群测试
用maven打jar包,需要添加的打包插件依赖
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
运行Maven package命令进行打包,将不带依赖的jar包上传到Hadoop集群
执行WordCount程序
hadoop jar wc.jar com.lppnb.mapreduce.wordcount.WordCountDriver /input /output
Hadoop序列化
概述
序列化就是把内存中的对象,转换成字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)以便于存储到磁盘(持久化)和网络传输。
反序列化就是将收到的字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)或者是磁盘的持久化数据,转换成内存中的对象。
为什么不用Java的序列化?
Java的序列化是一个重量级序列化框架(Serializable),一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额外的信息(各种校验信息,Header,继承体系等),不便于在网络中高效传输。所以Hadoop自己开发了一套序列化机制(Writable)。
Hadoop序列化特点:紧凑、快速、互操作
自定义bean对象
具体实现bean对象序列化步骤:
-
必须实现Writable接口
-
反序列化时,需要反射调用空参构造函数,所以必须有空参构造函数
public FlowBean() {} -
生成Getter和Setter方法
-
重写序列化方法
@Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeLong(upFlow); out.writeLong(downFlow); out.writeLong(sumFlow); } -
重写反序列化方法
@Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { upFlow = in.readLong(); downFlow = in.readLong(); sumFlow = in.readLong(); } -
注意反序列化的顺序和序列化的顺序完全一致
-
要想把结果显示在文件中,需要重写toString(),可用"\t"分开,方便后续用。
-
如果需要将自定义的bean放在key中传输,则还需要实现Comparable接口,因为MapReduce框架中的Shuffle过程要求key必须能排序。
@Override public int compareTo(FlowBean o) { // 倒序排列,从大到小 return this.sumFlow > o.getSumFlow() ? -1 : 1; }
MapReduce框架原理
InputFormat数据输入
切片与MapTask并行度决定机制
数据块:Block是HDFS物理上把数据分成一块一块。数据块是HDFS存储数据单位。
数据切片:数据切片只是在逻辑上对输入进行分片,并不会在磁盘上将其切分成片进行存储。数据切片是MapReduce程序计算输入数据的单位,一个切片会对应启动一个MapTask。
-
一个Job的map阶段并行度由客户端在提交Job时的切片数决定
-
每一个Split切片分配一个MapTask并行实例处理
-
默认情兄下,切片大小=BlockSize
-
切片时不考虑数据集整体,而是逐个针对每一个文件单独切片
Job提交流程
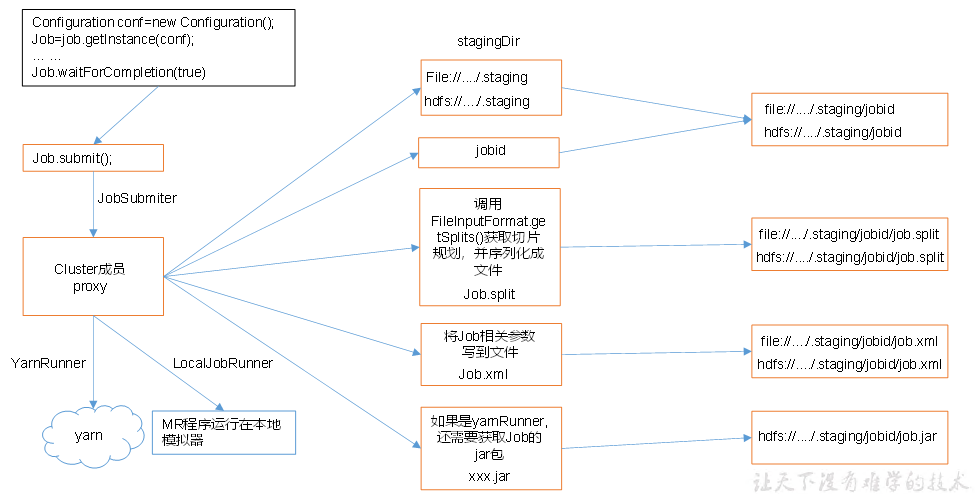
切片流程

切片大小参数配置

TextInputFormat
FileInputFormat常见的接口实现类包括:TextInputFormat、KeyValueTextInputFormat、NLineInputFormat、CombineTextInputFormat和自定义InputFormat等。
TextInputFormat是默认的FileInputFormat实现类。按行读取每条记录。键是存储该行在整个文件中的起始字节偏移量, LongWritable类型。值是这行的内容,不包括任何行终止符(换行符和回车符),Text类型。
CombineTextInputFormat
框架默认的TextInputFormat切片机制是对任务按文件规划切片,不管文件多小,都会是一个单独的切片,都会交给一个MapTask,这样如果有大量小文件,就会产生大量的MapTask,处理效率极其低下。
CombineTextInputFormat用于小文件过多的场景,它可以将多个小文件从逻辑上规划到一个切片中,这样,多个小文件就可以交给一个MapTask处理。
CombineTextInputFormat生成切片过程包括:虚拟存储过程和切片过程二部分:
虚拟存储过程:
将输入目录下所有文件大小,依次和设置的setMaxInputSplitSize值比较,如果不大于设置的最大值,逻辑上划分一个块。如果输入文件大于设置的最大值且大于两倍,那么以最大值切割一块;当剩余数据大小超过设置的最大值且不大于最大值2倍,此时将文件均分成2个虚拟存储块(防止出现太小切片)。
切片过程:
判断虚拟存储的文件大小是否大于setMaxInputSplitSize值,大于等于则单独形成一个切片。如果不大于则跟下一个虚拟存储文件进行合并,共同形成一个切片。

实现:
在Driver中添加代码
// 如果不设置InputFormat,它默认用的是TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
//虚拟存储切片最大值设置20m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 20971520);
MapReduce工作流程
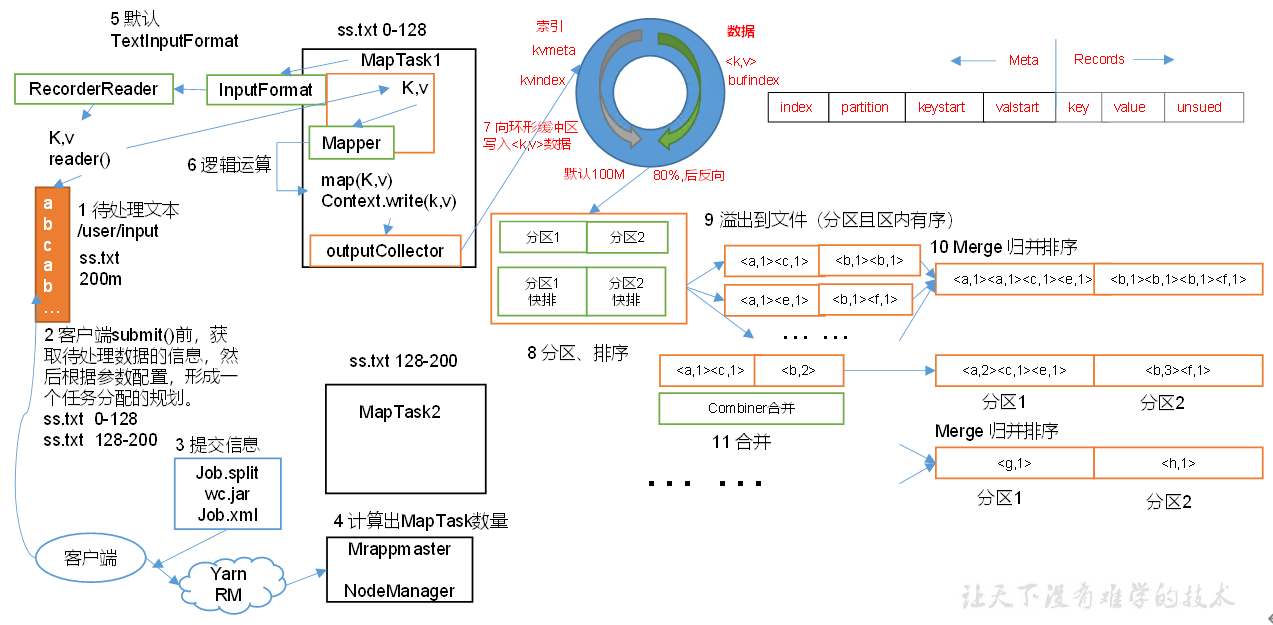
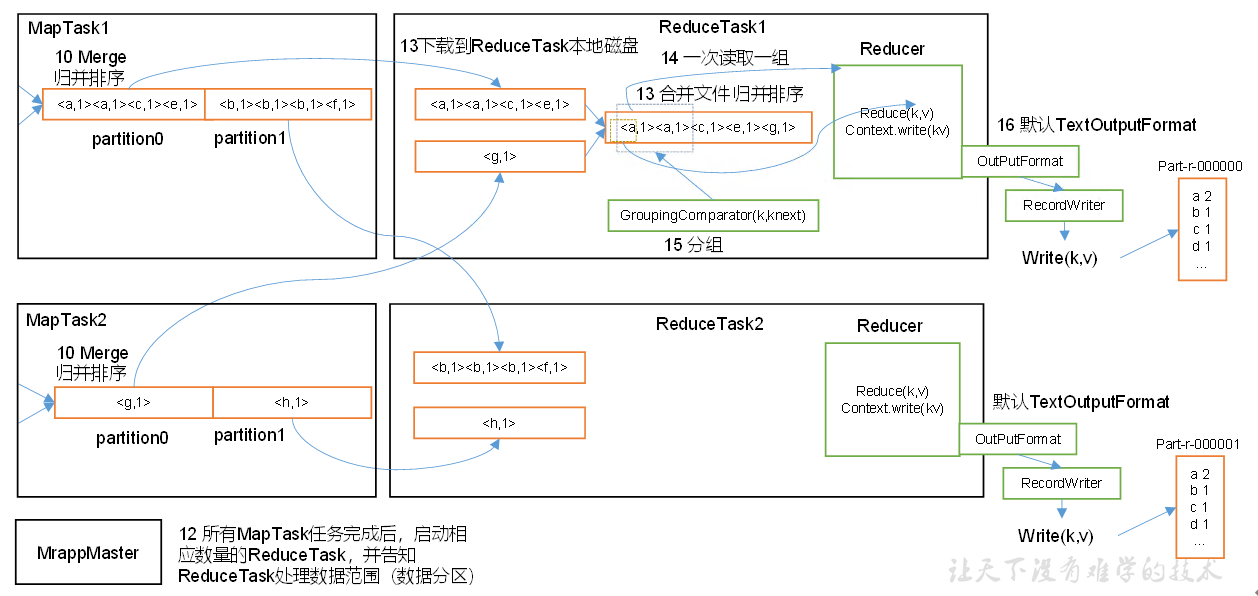
Shuffle中的缓冲区大小会影响到MapReduce程序的执行效率,原则上说,缓冲区越大,磁盘io的次数越少,执行速度就越快。
缓冲区的大小可以通过参数调整,参数:mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb默认100M。
Shuffle机制
Map方法之后,Reduce方法之前的数据处理过程称之为Shuffle。

Partition分区



WritableComparable排序
排序是MapReduce框架中最重要的操作之一。 MapTask和ReduceTask均会对数据按照key进行排序。该操作属于 Hadoop的默认行为。任何应用程序中的数据均会被排序,而不管逻辑上是否需要。默认排序是按照字典顺序排序。
对于MapTask,它会将处理的结果暂时放到环形缓冲区中,当环形缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次快速排序,并将这些有序数据溢写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完毕后,它会对磁盘上所有文件进行归并排序。
对于ReduceTask,它从每个MapTask上远程拷贝相应的数据文件,如果文件大小超过一定阈值,则溢写磁盘上,否则存储在内存中。如果磁盘上文件数目达到一定阈值,则进行一次归并排序以生成一个更大文件;如果内存中文件大小或者数目超过一定阈值,则进行一次合并后将数据谥写到磁盘上。当所有数据拷贝完毕后,ReduceTask统一对内存和磁盘上的所有数据进行一次归并排序。
排序分类:
-
部分排序
MapReduce根据输入记录的键对数据集排序。保证输出的每个文件内部有序。实现方式是设置多个ReduceTask。
-
全排序
最终输出结果只有一个文件,且文件内部有序。实现方式是只设置一个ReduceTask。
-
辅助排序:(GroupingComparator分组)
在Reduce端对key进行分组。应用于:在接收的key为bean对象时,想让一个或几个字段相同的key进入到同一个reduce方法时,可以采用分组排序。
-
二次排序
在自定义排序过程中,如果compareTo中的判断条件为两个即为二次排序。
自定义排序:
bean对象作为key传输,需要实现WritableComparable接口重写compareTo方法,就可以实现排序。
Combiner合并
-
Combiner是MR程序中Mapper和Reducer之外的一种组件。
-
Combiner组件的父类就是Reducer。.
-
Combiner和Reducer的区别在于运行的位置,Combiner是在每一个MapTask所在的节点运行, Reducer是接收全局所有Mapper的输出结果。
-
Combiner的意义就是对每一个MapTask的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量。
-
Combiner能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且,Combiner的输出kv应该跟Reducer的输入kv类型要对应起来。
比如求和可以使用Combiner,但是求平均值不行
自定义Combiner实现步骤:
自定义一个Combiner继承Reducer,重写Reduce方法
可以用Reducer当Combiner用
在Job驱动类中设置
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountCombiner.class);
OutputFormat数据输出
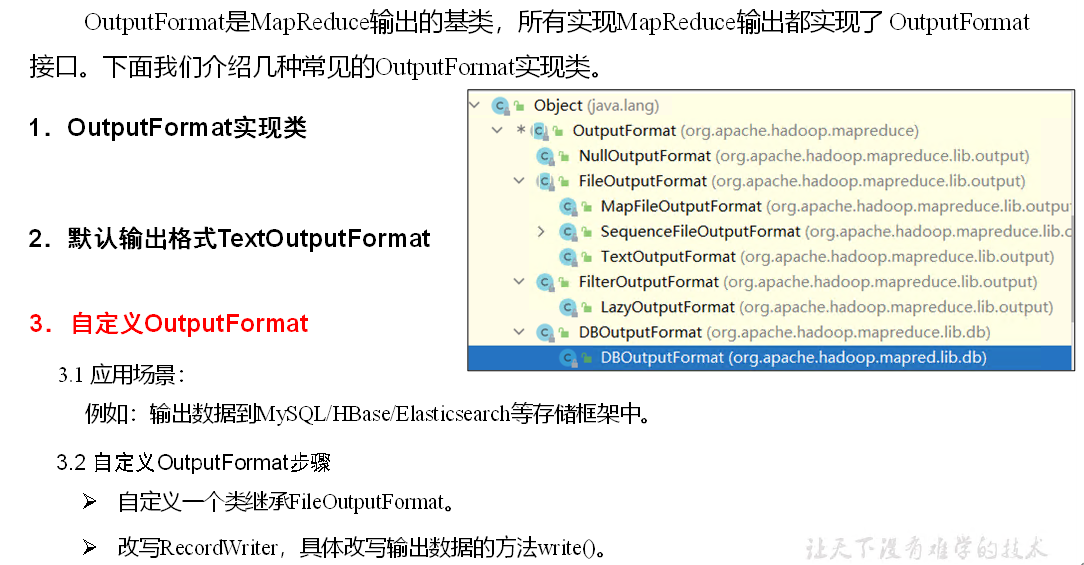
实现
自定义一个LogOutputFormat类
public class LogOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//创建一个自定义的RecordWriter返回
return new LogRecordWriter(job);
}
}
编写LogRecordWriter类
public class LogRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> {
private FSDataOutputStream atguiguOut;
private FSDataOutputStream otherOut;
public LogRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) {
try {
//获取文件系统对象
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
//用文件系统对象创建两个输出流对应不同的目录
atguiguOut = fs.create(new Path("d:/hadoop/atguigu.log"));
otherOut = fs.create(new Path("d:/hadoop/other.log"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String log = key.toString();
//根据一行的log数据是否包含atguigu,判断两条输出流输出的内容
if (log.contains("atguigu")) {
atguiguOut.writeBytes(log + "\n");
} else {
otherOut.writeBytes(log + "\n");
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//关流
IOUtils.closeStream(atguiguOut);
IOUtils.closeStream(otherOut);
}
}
LogDriver中添加代码
// 设置自定义的outputformat
job.setOutputFormatClass(LogOutputFormat.class);
ReduceTask
-
ReduceTask=0,表示没有Reduce阶段,输出文件个数和Map个数一致。
-
ReduceTask默认值就是1,所以输出文件个数为一个。
-
如果数据分布不均匀,就有可能在Reduce阶段产生数据倾斜
-
ReduceTask数量并不是任意设置,还要考虑业务逻辑需求,有些情况下,需要计算全局汇总结果,就只能有1个ReduceTask。
-
具体多少个ReduceTask需要根据集群性能而定。
一般情况下,ReduceTask的数量和MapTask的数量一样时效率最高
-
如果自定义分区数不是1,但是ReduceTask为1,是否执行分区过程。答案是:不执行分区过程。因为在MapTask的源码中,执行分区的前提是先判断ReduceNum个数是否大于1。大于1才执行。等于1的时候会走一个匿名内部类,partition总是返回0
Join应用
reduce join
Map端的主要工作:为来自不同表或文件的key/value对,打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
Reduce端的主要工作:在Reduce端以连接字段作为key的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在Map阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行合并就ok了。
缺点:这种方式中,合并的操作是在Reduce阶段完成,Reduce端的处理压力太大,Map节点的运算负载则很低,资源利用率不高,且在Reduce阶段极易产生数据倾斜。
代码实现:
创建商品和订单合并后的TableBean类
public class TableBean implements Writable {
private String id; //订单id
private String pid; //产品id
private int amount; //产品数量
private String pname; //产品名称
private String flag; //判断是order表还是pd表的标志字段
public TableBean() {
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(String pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPname() {
return pname;
}
public void setPname(String pname) {
this.pname = pname;
}
public String getFlag() {
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(String flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "\t" + pname + "\t" + amount;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(id);
out.writeUTF(pid);
out.writeInt(amount);
out.writeUTF(pname);
out.writeUTF(flag);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.id = in.readUTF();
this.pid = in.readUTF();
this.amount = in.readInt();
this.pname = in.readUTF();
this.flag = in.readUTF();
}
}
编写TableMapper类
public class TableMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,TableBean> {
private String filename;
private Text outK = new Text();
private TableBean outV = new TableBean();
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取对应文件名称
InputSplit split = context.getInputSplit();
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit) split;
filename = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取一行
String line = value.toString();
//判断是哪个文件,然后针对文件进行不同的操作
if(filename.contains("order")){ //订单表的处理
String[] split = line.split("\t");
//封装outK
outK.set(split[1]);
//封装outV
outV.setId(split[0]);
outV.setPid(split[1]);
outV.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(split[2]));
outV.setPname("");
outV.setFlag("order");
}else { //商品表的处理
String[] split = line.split("\t");
//封装outK
outK.set(split[0]);
//封装outV
outV.setId("");
outV.setPid(split[0]);
outV.setAmount(0);
outV.setPname(split[1]);
outV.setFlag("pd");
}
//写出KV
context.write(outK,outV);
}
}
编写TableReducer类
public class TableReducer extends Reducer<Text,TableBean,TableBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<TableBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ArrayList<TableBean> orderBeans = new ArrayList<>();
TableBean pdBean = new TableBean();
for (TableBean value : values) {
//判断数据来自哪个表
if("order".equals(value.getFlag())){ //订单表
//创建一个临时TableBean对象接收value
TableBean tmpOrderBean = new TableBean();
try {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(tmpOrderBean,value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//将临时TableBean对象添加到集合orderBeans
orderBeans.add(tmpOrderBean);
}else { //商品表
try {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pdBean,value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//遍历集合orderBeans,替换掉每个orderBean的pid为pname,然后写出
for (TableBean orderBean : orderBeans) {
orderBean.setPname(pdBean.getPname());
//写出修改后的orderBean对象
context.write(orderBean,NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
编写TableDriver类
public class TableDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(TableDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(TableMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(TableReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(TableBean.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(TableBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:\\input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\output"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
map join
map join适用于一张表十分小、一张表很大的场景。
具体办法:采用DistributedCache
-
在Mapper的setup阶段,将文件读取到缓存集合中
-
在Driver驱动类中加载缓存
// 缓存普通文件到Task运行节点。 job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///e:/cache/pd.txt")); // 如果是集群运行,需要设置HDFS路径 job.addCacheFile(new URI("hdfs://hadoop102:8020/cache/pd.txt"));
代码实现:
先在MapJoinDriver驱动类中添加缓存文件
public class MapJoinDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, URISyntaxException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
// 1 获取job信息
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// 2 设置加载jar包路径
job.setJarByClass(MapJoinDriver.class);
// 3 关联mapper
job.setMapperClass(MapJoinMapper.class);
// 4 设置Map输出KV类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 5 设置最终输出KV类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 加载缓存数据
job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///D:/input/tablecache/pd.txt"));
// Map端Join的逻辑不需要Reduce阶段,设置reduceTask数量为0
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
// 6 设置输入输出路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:\\input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\output"));
// 7 提交
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
在MapJoinMapper类中的setup方法中读取缓存文件
public class MapJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
private Map<String, String> pdMap = new HashMap<>();
private Text text = new Text();
//任务开始前将pd数据缓存进pdMap
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//通过缓存文件得到小表数据pd.txt
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
Path path = new Path(cacheFiles[0]);
//获取文件系统对象,并开流
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
FSDataInputStream fis = fs.open(path);
//通过包装流转换为reader,方便按行读取
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8"));
//逐行读取,按行处理
String line;
while (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line = reader.readLine())) {
//切割一行
//01 小米
String[] split = line.split("\t");
pdMap.put(split[0], split[1]);
}
//关流
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//读取大表数据
//1001 01 1
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");
//通过大表每行数据的pid,去pdMap里面取出pname
String pname = pdMap.get(fields[1]);
//将大表每行数据的pid替换为pname
text.set(fields[0] + "\t" + pname + "\t" + fields[2]);
//写出
context.write(text,NullWritable.get());
}
}
数据清洗(ETL)
ETL,是英文Extract-Transform-Load的缩写,用来描述将数据从来源端经过抽取(Extract)、转换(Transform)、加载(Load)至目的端的过程。
在运行核心业务MapReduce程序之前,往往要先对数据进行清洗,清理掉不符合用户要求的数据。清理的过程往往只需要运行Mapper程序,不需要运行Reducer程序。
Hadoop数据压缩
概述
压缩的优点:减少磁盘IO、减少磁盘存储空间。
压缩的缺点:增加CPU开销。
压缩原则:
-
运算密集型的Job,少用压缩
-
IO密集型的Job,多用压缩
MR支持的压缩编码
| 压缩格式 | Hadoop自带? | 算法 | 文件扩展名 | 是否可切片 | 换成压缩格式后,原来的程序是否需要修改 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEFLATE | 是,直接使用 | DEFLATE | .deflate | 否 | 和文本处理一样,不需要修改 |
| Gzip | 是,直接使用 | DEFLATE | .gz | 否 | 和文本处理一样,不需要修改 |
| bzip2 | 是,直接使用 | bzip2 | .bz2 | 是 | 和文本处理一样,不需要修改 |
| LZO | 否,需要安装 | LZO | .lzo | 是 | 需要建索引,还需要指定输入格式 |
| Snappy | 是,直接使用 | Snappy | .snappy | 否 | 和文本处理一样,不需要修改 |
压缩方式选择
Gzip压缩
优点:压缩率比较高;
缺点:不支持Split;压缩/解压速度一般;
Bzip2压缩
优点:压缩率高;支持Split;
缺点:压缩/解压速度慢。
Lzo压缩
优点:压缩/解压速度比较快;支持Split;
缺点:压缩率一般;想支持切片需要额外创建索引。
Snappy压缩
优点:压缩和解压缩速度快;
缺点:不支持Split;压缩率一般;

压缩参数配置
为了支持多种压缩/解压缩算法,Hadoop引入了编码/解码器
| 压缩格式 | 对应的编码/解码器 |
|---|---|
| DEFLATE | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec |
| gzip | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec |
| bzip2 | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec |
| LZO | com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec |
| Snappy | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec |
要在Hadoop中启用压缩,可以配置如下参数
| 参数 | 默认值 | 阶段 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|---|
| io.compression.codecs (在core-site.xml中配置) | 无,这个需要在命令行输入hadoop checknative查看 | 输入压缩 | Hadoop使用文件扩展名判断是否支持某种编解码器 |
| mapreduce.map.output.compress(在mapred-site.xml中配置) | false | mapper输出 | 这个参数设为true启用压缩 |
| mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec(在mapred-site.xml中配置) | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec | mapper输出 | 企业多使用LZO或Snappy编解码器在此阶段压缩数据 |
| mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress(在mapred-site.xml中配置) | false | reducer输出 | 这个参数设为true启用压缩 |
| mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec(在mapred-site.xml中配置) | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec | reducer输出 | 使用标准工具或者编解码器,如gzip和bzip2 |
Map输出端采用压缩
在Driver中添加代码
// 开启map端输出压缩
conf.setBoolean("mapreduce.map.output.compress", true);
// 设置map端输出压缩方式
conf.setClass("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", BZip2Codec.class,CompressionCodec.class);
Reduce输出端采用压缩
在Driver中添加代码
// 设置reduce端输出压缩开启
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
// 设置压缩的方式
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, BZip2Codec.class);
