Vuex 核心技术
State/Muation/Action
-
State:
- State 的作用就是存储数据, Vuex 是状态管理框架,所以在 Vuex 中 state 表示数据在 Vuex 中的存储状态,你可以把它看成一个全局的(Vue 应用中可以到处访问)大 JSON 对象。
-
Muation:
- Muation的作用很纯粹,那就是修改 State 状态的,State 的数据是不能被直接修改的,你如果要更新 State 状态值你只能借助于 Muation 来完成。
- Muation 是一个函数,接收两个参数
- state:当前上下文的 state 实例,可以通过这个参数修改 state 值,比如
state.count=12就可以完成 State 中 count 对象的修改 - payload:接收外部传入的对象,需要和调用方约定好对象类型,也可以不传参数
- state:当前上下文的 state 实例,可以通过这个参数修改 state 值,比如
-
Action:
-
Vuex 对数据管理的非常严格,除了只能通过 mutation 修改 state 状态外,还不允许外部调用 mutation 函数。如果想要在 vue 中修改 state 值,那么你只能通过 Vuex 的 Action 来触发 mutation 函数执行修改。
-
action 是一个函数,它接收两个参数:
-
第一个参数是 context 对象(Vuex 的上下文值) context 对象包含以下属性或方法
{ state, // 等同于 `store.state`,若在模块中则为局部状态 rootState, // 等同于 `store.state`,只存在于模块中, commit, // 等同于 `store.commit` dispatch, // 等同于 `store.dispatch` getters, // 等同于 `store.getters` rootGetters; // 等同于 `store.getters`,只存在于模块中 } -
第二个参数是接收外部传递的参数
-
commit:commit 是个函数,它的作用就是把数据提交到 mutation 中,同样它也是有两个参数,第一个参数是 mutation 的函数名称,第二个参数是自定义的对象
-
state:这里的 state 只能取值,不能修改值
-

-
rootState只能在第三个参数位置上
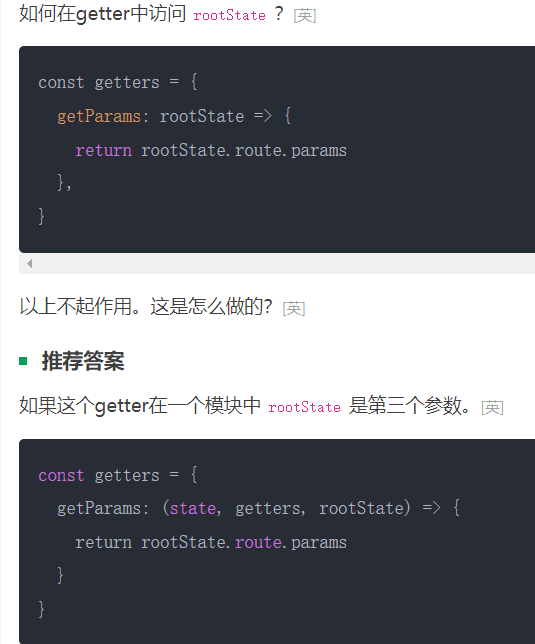
-
-
-
store写法
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.count++; }, decrement(state) { state.count--; } }, actions: { increment: ({ commit }) => commit('increment'), decrement: ({ commit }) => commit('decrement') } }); -
获取 state:
- 在任意的 vue 文件中,你可以通过
$store.state.count来获取 state 中的 count 属性值。state 只支持单向绑定,当 mutation 更新了 state 状态后,vue 中的值也会自动更新 - 借助 Vuex 的 mapState 函数,这个函数可以动态的将 state 和 computed 绑定上。使用 computed 和 mapState 组合方案的好处是页面只会根据 count 值变化而刷新页面,而不会因为 state 的变化就会触发页面刷新
- 在任意的 vue 文件中,你可以通过
-
执行 store 的 action:
- 可以通过
mapActions这个 vuex 的函数把 store 的 action 绑定到 vue 的 methods 对象里
- 可以通过
-
<template> <div> Clicked: {{ count }} times <div> <button @click="increment">+</button> <button @click="decrement">-</button> </div> </div> </template> <script> // 导入 mapState mapActions 函数 import { mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'; export default { computed: { ...mapState({ count: state => state.count }) }, methods: { ...mapActions(['increment', 'decrement']) } }; </script>
Getter
-
Vuex 的 Getter 函数就是类似 Vue computed 函数的作用,相当于是store的computed ,Getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
-
定义Getter:
-
Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数
getters: { evenOrOdd: state => (state.count % 2 === 0 ? "偶数" : "奇数") }
-
-
使用 Getter:
-
类似 state 的使用方式一样,你也可以使用 mapGetters 函数来完成映射
-
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default { // ... computed: { // 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中 ...mapGetters([ 'evenOrOdd' ]) } }
-
Vuex request
-
import Vue from "vue"; import Vuex from "vuex"; import axios from "axios"; Vue.use(Vuex); export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { user: {} }, mutations: { setUser(state, payload) { state.user = payload; } }, actions: { login: async ({ commit }, param) => { // 执行远程请求 const response = await axios.post( "https://www.fastmock.site/mock/a9b15cd4db90d4e03ed76cd3c76d9197/f6/login", { username: param.username, password: param.password } ); if (response.data.success) { commit("setUser", response.data.data); } } } });
Vuex模块
配置模块
-
Vuex 模块简单来说就是把一个 store 文件分割成多个 js 文件,每个分割的文件就是一个模块,每个模块都拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter,甚至模块还可以嵌套子模块
-
多个模块在一个文件里:
const moduleA = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { ... } } const moduleB = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA, b: moduleB } }) -
获取一个模块:
store.state.a; // -> moduleA 的状态 store.state.b; // -> moduleB 的状态 -
分拆模块文件:
-
//count.js export default { namespaced: true, state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.count++; }, decrement(state) { state.count--; } }, actions: { increment: ({ commit }) => commit("increment"), decrement: ({ commit }) => commit("decrement") }, }; //namespaced: true 这个代表的是开启命名空间,这个设置的作用在于这个 module 的 state、mutation、action、getter 都限定在本 module 里,这样就不会污染别的 module,比如说两个 module 的 action 名称一样是没有关系的。 -
集成 module:
//index.js import Vue from "vue"; import Vuex from "vuex"; Vue.use(Vuex); import count from "./count"; export default new Vuex.Store({ modules: { count:count } }); //modules 对象里添加的属性名称就是 module 的名称 -
vue 中使用 module store:
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from "vuex"; const { mapState, mapActions } = createNamespacedHelpers("count"); const { mapState:demoMapState, mapActions:demoMapActions} = createNamespacedHelpers("demo"); //使用变量别名的方式把两个module区分开 export default { computed: { ...mapState({ count: state => state.count }), ...demoMapState({ demoCount: state => state.count }) }, methods: { ...mapActions(["increment", "decrement"]) } }; -
在当前模块中调用其他模块的mutation函数
commit( "products/decrementProductInventory",// 命名空间/mutation 函数名称 { id: product.id }, //decrementProductInventory 函数的第二个参数 { root: true } //设置为在全局命名空间内分发 ); -
在当前模块中调用其他模块的action函数
actions: { async demo({ state, commit,dispatch }) { // 触发 product module的 getAllProducts 这个 action dispatch('product/getAllProducts', null, { root: true }) } } -
在当前模块中调用其他模块的state:rootState.xxx
-
在当前模块中调用其他模块的getter:rootGetters['xxx']
-
-
… 操作符(也被叫做延展操作符)用于取出参数对象的所有可遍历属性,然后拷贝到当前对象之中。它允许传递数组或者类数组直接做为函数的参数而不用通过apply。延展操作符一般用于属性的批量赋值上。
